Proposals
Stages at LFD / IRL

 The drag forces in wake flows are a major contributor to the energy consumption in many industrial applications, especially in the transportation sector. Strategies in flow control require a solid knowledge of the physical mechanisms that characterize
wake flows. Fundamental aspects of two-and three-dimensional transitions, can be raised from the study of flow dynamics over a rectangular inclined plate. Let us remind that that the wake of a plate normal to a flow is characterized by two rows of
counter-rotating vortices, namely the Bénard-von Kármán vortex street. It has been studied both experimentally and analytically since the early work of von Kármán [1]. On the contrary, when the flow is parallel to a flat plate, a boundary layer problem
is presented. Between these two limits, the flow over an inclined plate presents an interesting behavior first approached by Fage and Johansen [2]. Later Abernathy [3] contributed with a model and measurements for the vortex shedding frequency and
the separation of the free-streamline patterns. A literature review on the inclined plate is available in [4], which analyzes the effect of plate aspect ratio using large eddy simulations. However, the authors overlook the historical findings by Eiffel [5]
that measure drag forces presented in Figure 1. Therefore, we suggest the following activities:
The drag forces in wake flows are a major contributor to the energy consumption in many industrial applications, especially in the transportation sector. Strategies in flow control require a solid knowledge of the physical mechanisms that characterize
wake flows. Fundamental aspects of two-and three-dimensional transitions, can be raised from the study of flow dynamics over a rectangular inclined plate. Let us remind that that the wake of a plate normal to a flow is characterized by two rows of
counter-rotating vortices, namely the Bénard-von Kármán vortex street. It has been studied both experimentally and analytically since the early work of von Kármán [1]. On the contrary, when the flow is parallel to a flat plate, a boundary layer problem
is presented. Between these two limits, the flow over an inclined plate presents an interesting behavior first approached by Fage and Johansen [2]. Later Abernathy [3] contributed with a model and measurements for the vortex shedding frequency and
the separation of the free-streamline patterns. A literature review on the inclined plate is available in [4], which analyzes the effect of plate aspect ratio using large eddy simulations. However, the authors overlook the historical findings by Eiffel [5]
that measure drag forces presented in Figure 1. Therefore, we suggest the following activities:
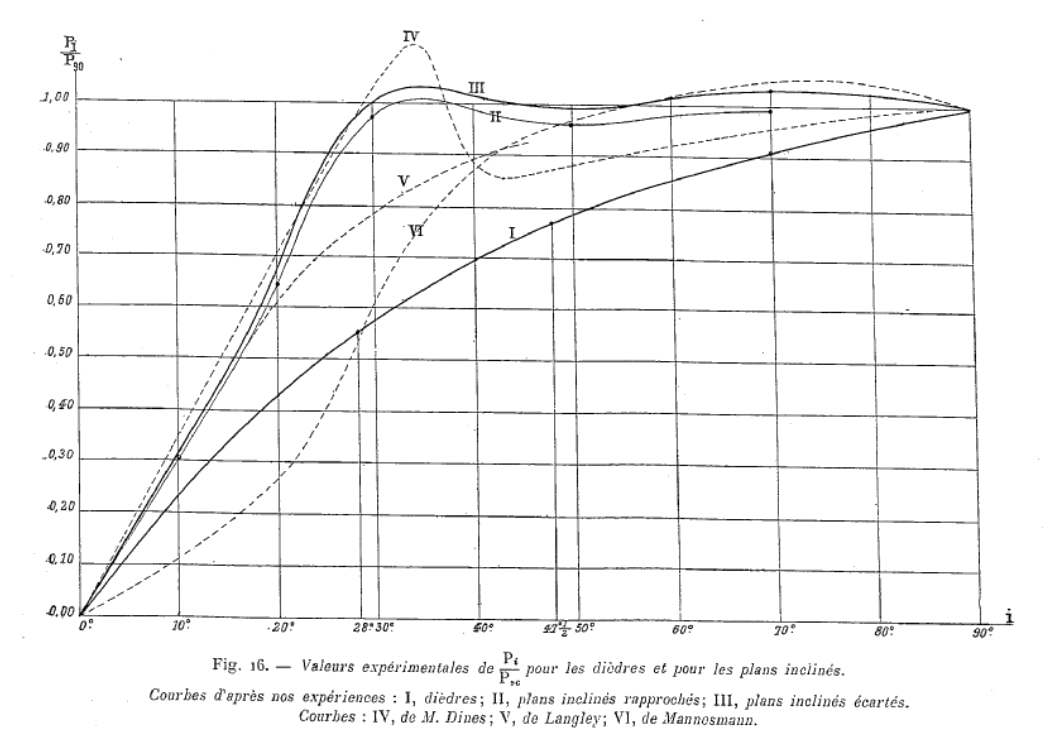
Figure 1. Drag forces on an inclined plate
[1] T. von Kármán. Über den mechanismus des widerstandes, den ein bewegter körper in einer flüssigkeit erfährt. Nachr. Ges. Wissenschaft. Göttingen, pages 509–517, 1911.
[2] Arthur Fage and FC Johansen. On the flow of air behind an inclined flat plate of infinite span. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character, 116(773):170–197, 1927.
[3] F. H. Abernathy. Flow Over an Inclined Plate. Journal of Basic Engineering, 84(3): 380–388, 09 1962.
[4] Mehrdad Shademan and Arash Naghib-Lahouti. Effects of aspect ratio and inclination angle on aerodynamic loads of a flat plate. Advances in Aerodynamics, 2(1):1–23, 2020.
[5] Gustave Eiffel. Recherches expérimentales sur la résistance de l’air exécutées à la tour Eiffel. L. Maretheux, 1907.